Tenth Amendment Center: Hawaii Bill Would Ban Warrantless Stingray Spying, Take on Federal Surveillance State
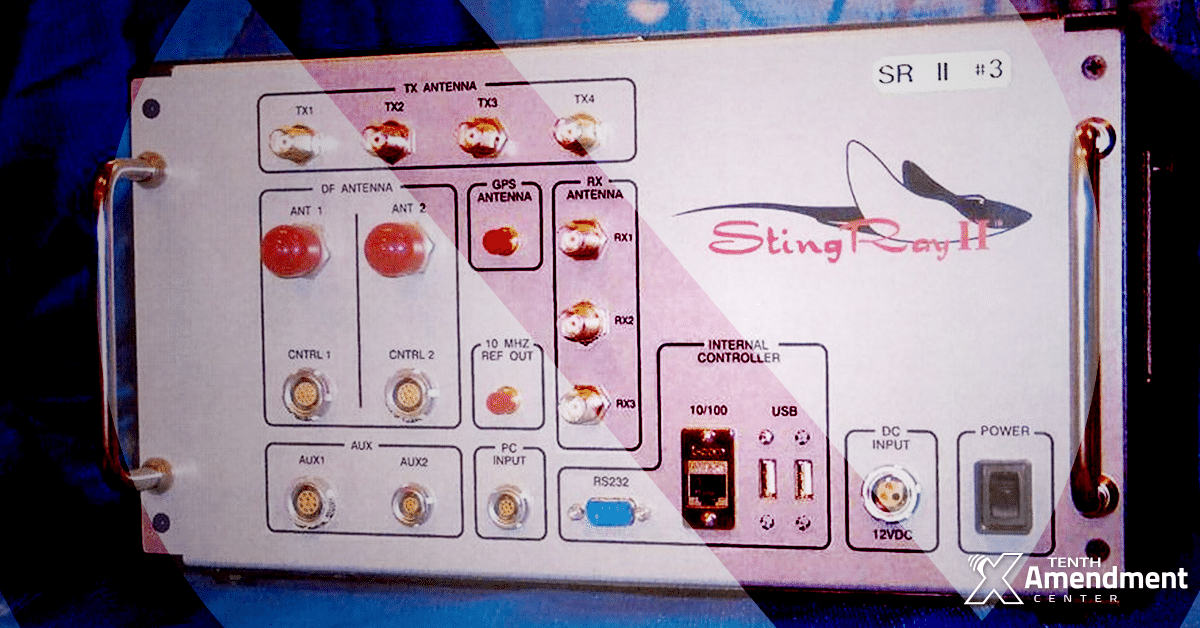
HONOLULU, Hawaii (Dec. 26, 2019) – A bill filed in the Hawaii Senate would ban the use of “stingrays” to track the location of phones and sweep up electronic communications without a warrant or court order in most situations. The proposed law would not only protect privacy in Hawaii; it would also hinder one aspect of the federal surveillance state.
Sen. Russell Ruderman (D), along with three cosponsors, introduced Senate Bill 465 (SB465) last January and it will carry over into the 2020 legislative session. The legislation would help block the use of cell-site simulators, known as “stingrays.” These devices essentially spoof cell phone towers, tricking any device within range into connecting to the stingray instead of the tower, allowing law enforcement to sweep up communications content, as well as locate and track the person in possession of a specific phone or other electronic device.
SB465 would prohibit any state or local agency, including law enforcement, from collecting or using a person’s electronic data or metadata by means of a cell-site simulator without a warrant based on probable cause in most situations. The bill provides for three exceptions to the warrant requirement.
- The person’s informed consent
- Actions in accordance with a legally recognized exception to the warrant requirement.
- An emergency involving the danger of death or serious bodily injury.
SB465 would also include cell-site simulators under existing wiretapping laws. It would place the same legal requirements on stingray use that currently exist to authorize a landline wiretap. Under the proposed law, police will be required to get a court order or warrant before listening to conversations using a stingray device in most situations.
IMPACT ON FEDERAL SURVEILLANCE PROGRAMS
The federal government funds the vast majority of state and local stingray programs, attaching one important condition. The feds require agencies acquiring the technology to sign non-disclosure agreements. This throws a giant shroud over the program, even preventing judges, prosecutors and defense attorneys from getting information about the use of stingrays in court. The feds actually instruct prosecutors to withdraw evidence if judges or legislators press for information. As the Baltimore Sun reported in April 2015, a Baltimore detective refused to answer questions on the stand during a trial, citing a federal non-disclosure agreement.
Defense attorney Joshua Insley asked Cabreja about the agreement.
“Does this document instruct you to withhold evidence from the state’s attorney and Circuit Court, even upon court order to produce?” he asked.
“Yes,” Cabreja said.
As privacysos.org put it, “The FBI would rather police officers and prosecutors let ‘criminals’ go than face a possible scenario where a defendant brings a Fourth Amendment challenge to warrantless stingray spying.”
The experience of a Pinellas County, Florida, man further highlights the shroud of secrecy around the use of stingray devices, along with the potential for abuse of power inherent in America’s law enforcement community.
The feds sell the technology in the name of “anti-terrorism” efforts. With non-disclosure agreements in place, most police departments refuse to release any information on the use of stingrays. But information obtained from the Tacoma Police Department revealed that it uses the technology primarily for routine criminal investigations.
Some privacy advocates argue that stingray use can never happen within the parameters of the Fourth Amendment because the technology necessarily connects to every electronic device within range, not just the one held by the target. And the information collected by these devices undoubtedly ends up in federal databases.
The feds can share and tap into vast amounts of information gathered at the state and local level through fusion centers and a system known as the “information sharing environment” or ISE. In other words, stingrays create the potential for the federal government to track the movement of millions of Americans with no warrant, no probable cause, and without the people even knowing it.
Fusion centers were sold as a tool to combat terrorism, but that is not how they are being used. The ACLU pointed to a bipartisan congressional report to demonstrate the true nature of government fusion centers: “They haven’t contributed anything meaningful to counterterrorism efforts. Instead, they have largely served as police surveillance and information sharing nodes for law enforcement efforts targeting the frequent subjects of police attention: Black and brown people, immigrants, dissidents, and the poor.”
Fusion centers operate within the broader ISE. According to its website, the ISE “provides analysts, operators, and investigators with information needed to enhance national security. These analysts, operators, and investigators…have mission needs to collaborate and share information with each other and with private sector partners and our foreign allies.” In other words, ISE serves as a conduit for the sharing of information gathered without a warrant. Known ISE partners include the Office of Director of National Intelligence which oversees 17 federal agencies and organizations, including the NSA. ISE utilizes these partnerships to collect and share data on the millions of unwitting people they track.
The federal government encourages and funds stingrays at the state and local level across the U.S., thereby undoubtedly gaining access to a massive data pool on Americans without having to expend the resources to collect the information itself. By placing restrictions on stingray use, state and local governments limit the data available that the feds can access.
In a nutshell, without state and local cooperation, the feds have a much more difficult time gathering information. Enactment of SB465 would strike a major blow to the surveillance state and would be a win for privacy.
WHAT’S NEXT
SB465 will be officially introduced and assigned to a committee when the Hawaii General Assembly regular session begins Jan. 15. It will have to pass committee by a majority vote before moving forward in the legislative process.
Mike Maharrey
December 26, 2019 at 10:50AM
